How to Lower CPU Temperature on PCs and Laptops: All Methods

If your CPU is overheating during overclocking, when launching applications or games, it's essential to identify the cause of the malfunction. There are many ways to lower the temperature of the central processing unit — from simple to advanced. In this guide, we will explain why the CPU temperature might rise and describe all effective methods to reduce it.
How to Check CPU Temperature
Every motherboard is equipped with sensors that allow you to check the temperature of almost any component in your PC. However, this should be done using special software. In this material, we've discussed the easiest applications to use for monitoring the central processor's temperature, as well as answered other possible questions.
What is the Normal CPU Temperature
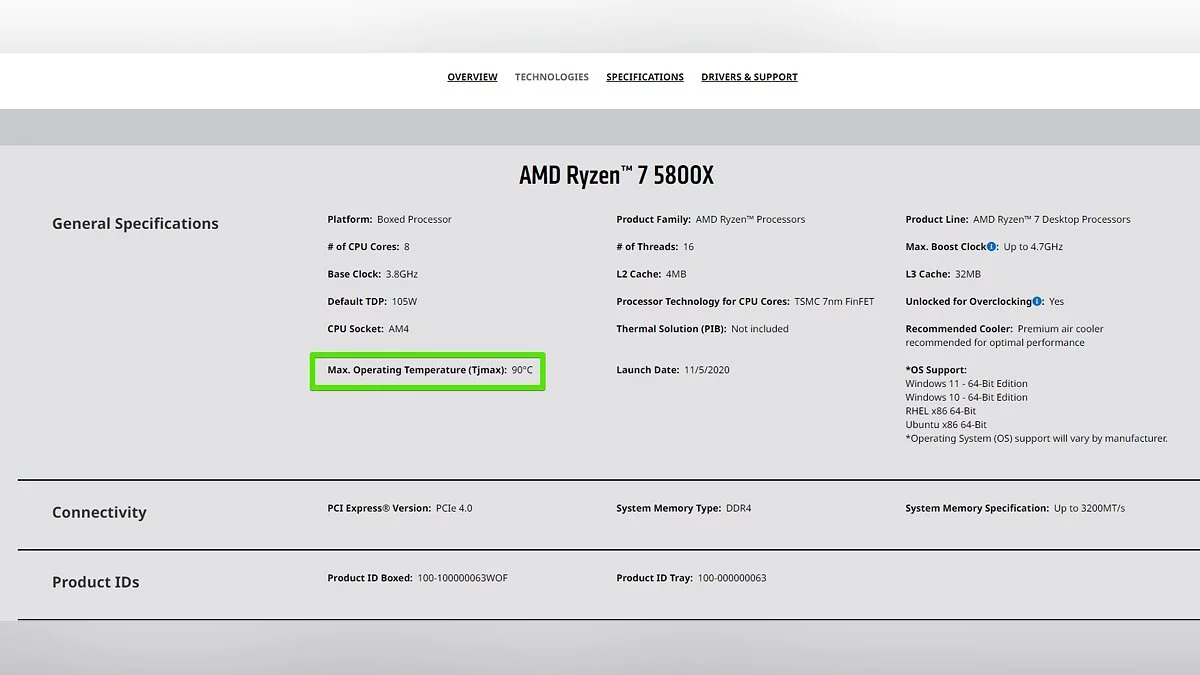
The operating temperature varies for each CPU model, but it should not exceed 90-95 degrees Celsius, as this negatively affects not only its performance but can also damage the system component.
To check the operating temperature of your CPU, simply visit the developer's official website and look up the component's parameters by model or serial number. For example, the maximum operating temperature for my processor is 90 degrees Celsius. Anything above this is not normal and can negatively impact the device in the long term.
Remove the Side Panel
If the CPU has reached its maximum temperature and you urgently need to cool it down without turning off the device, just remove the side panel of your PC case. This will disrupt the direct airflow from the fans, but it will allow much more cool air into the system, and the CPU temperature will drop by a few degrees. Another good option is to lay the case on its side so that the hot air rises and immediately exits the case.
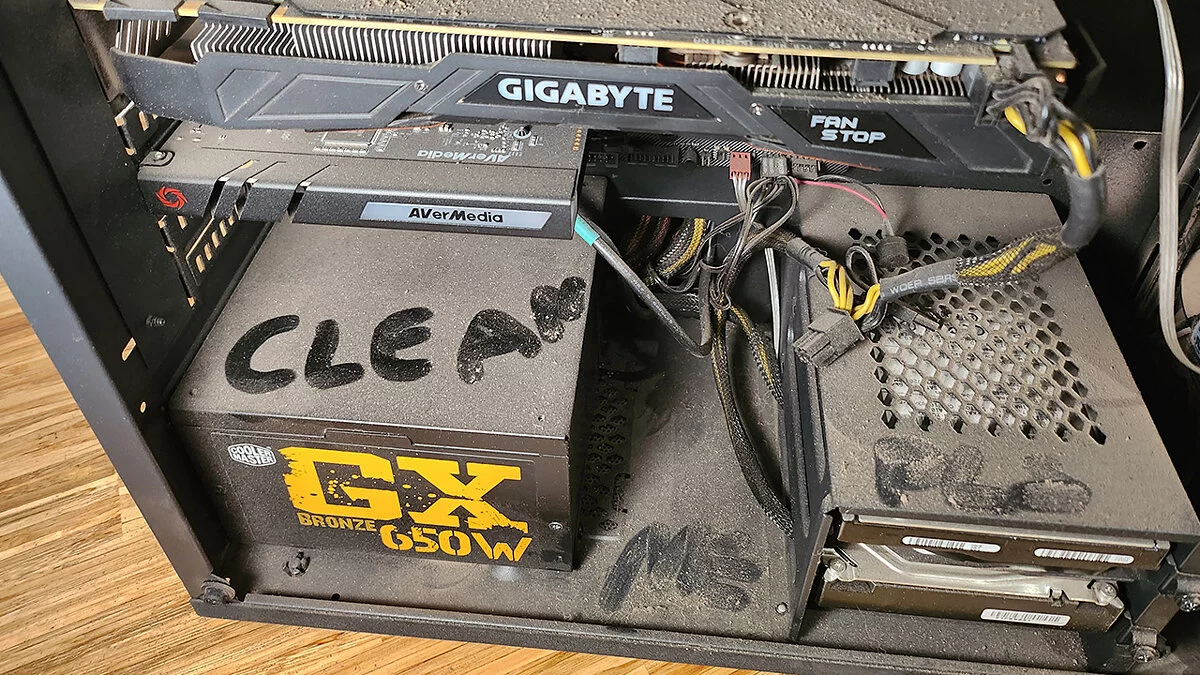
Clean the PC Case from Dust
We all know that cleaning the PC from dust should be done regularly, but few of us actually do it. Cleaning the computer is one of the best ways to quickly and inexpensively lower the central processing unit's temperature. Dust clogs the coolers' radiators, preventing cool air from reaching the main components, and a clogged CPU cooler will have to exert additional effort to cope with the layer of dust.
Additionally, cable management can also affect the temperatures of components inside the PC, as the cooler air needs to reach the CPU cooler without any obstacles. If it has to navigate through cables and nooks, less cool air will reach the radiator, leading to higher temperatures.
Optimize Airflow in the PC Case
If you can't lower the CPU temperature and other components inside the computer case, you need to optimize the airflow in your PC case. Using the schemes shown below, you can increase the speed of hot air removal from the case, by introducing cool air from the bottom and expelling it at the top. This way, you create an air tunnel that carries away the heat from all components inside the case, including the central processor.
If your PC's fans are installed differently than shown in the schemes above, try reassembling them and conducting a stress test on your computer. You will be pleasantly surprised.
Use a Cooling Pad for Your Laptop
If your laptop constantly overheats even after cleaning and replacing the thermal paste on the CPU, you can use a cooling pad for laptops, which helps to lower the temperature and avoid overheating of the device. Such pads are made from materials capable of absorbing heat and dissipating it, and are also equipped with fans that improve air circulation.
Increase Fan Speed
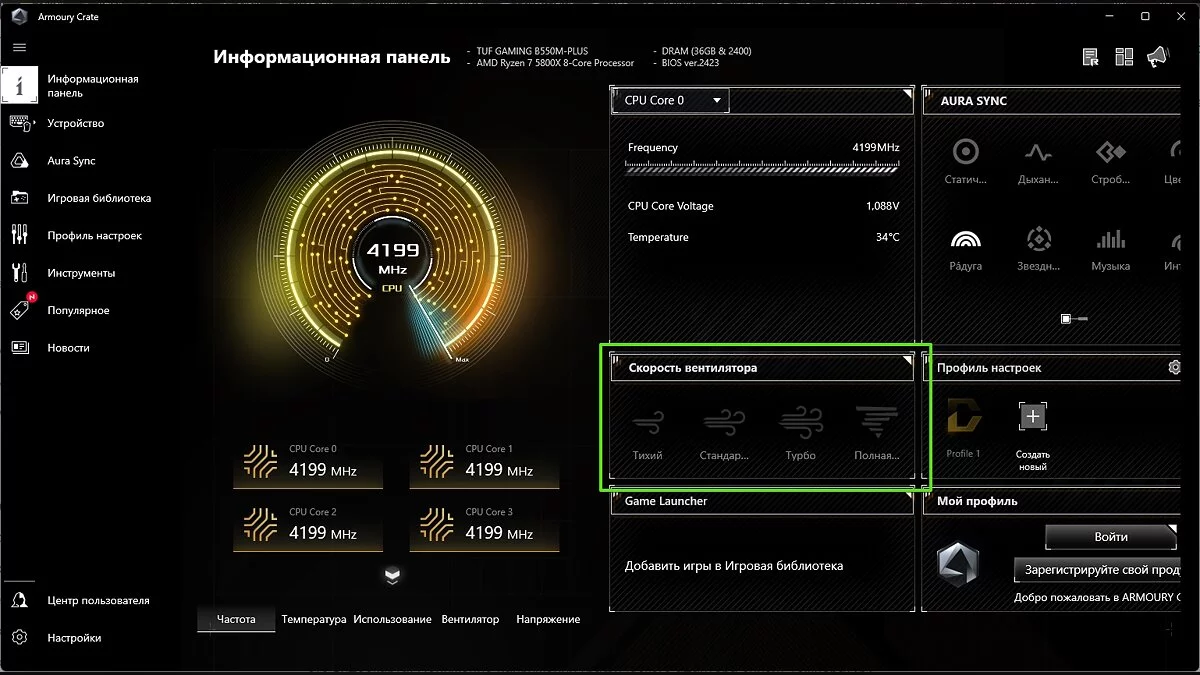
In emergency cases, you can resort to a quite effective method — increasing the speed of the fans on the central processor's radiator. To do this, switch all system fans to performance mode in UEFI/BIOS. Alternatively, you can do this through the CPU manufacturer's own application. It should be noted that in this case, the fans will start to make a loud hum, which will interfere with the comfortable use of the PC.
Modern motherboards come with special applications that allow you to adjust the fan speed. For example, for Asus motherboards, you can install the Armoury Crate program.
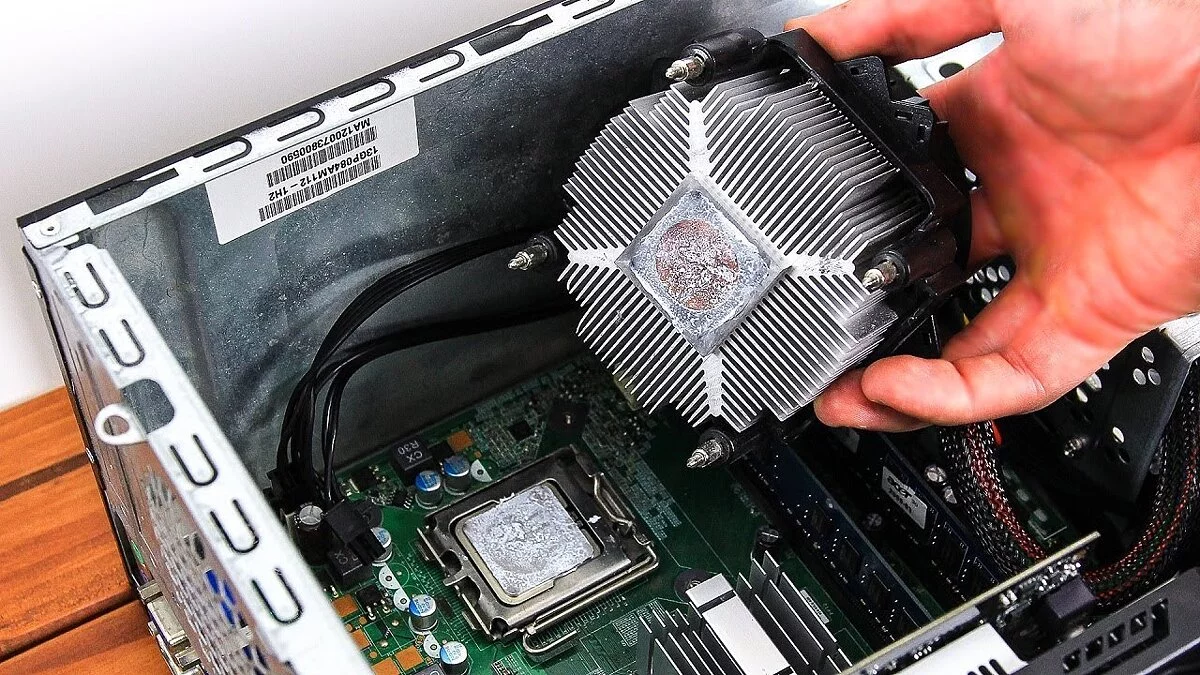
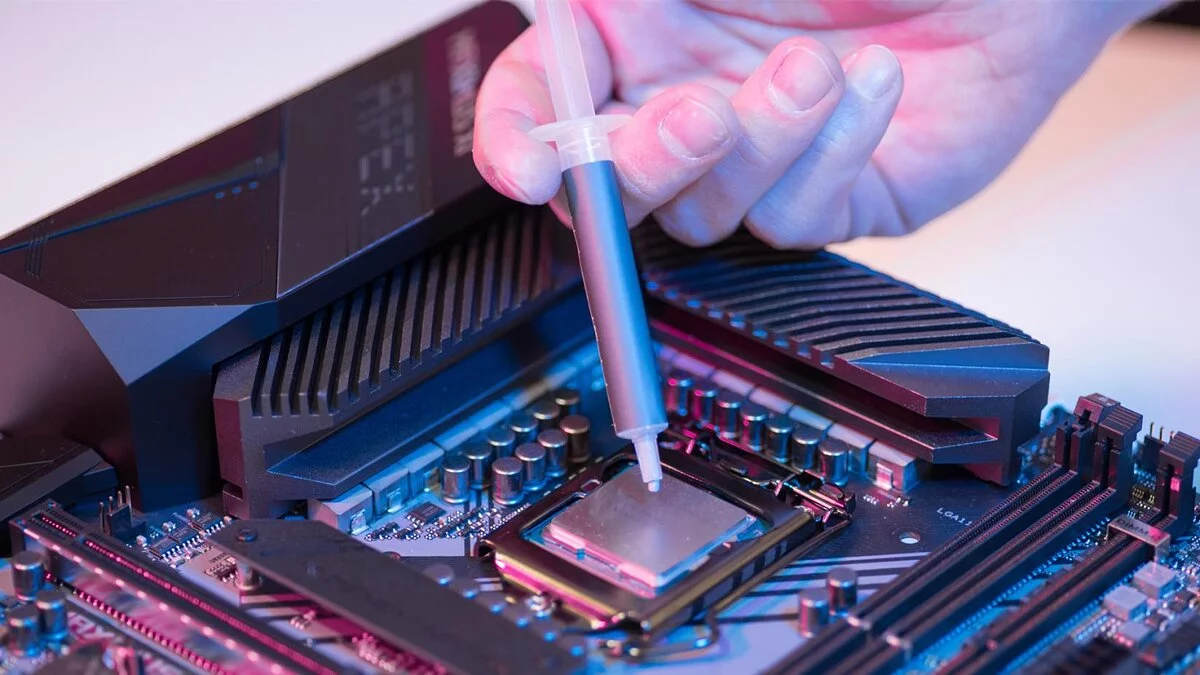
Replace the Cooling Paste (Thermal Paste)
If your machine is overheating (fans are running at maximum speed, but the CPU temperature is not decreasing), applying a fresh layer of thermal paste can boost performance while simultaneously lowering the CPU temperature and extending the lifespan of components. To do this, follow the instructions:
- Turn on the computer and let it run for a few minutes before turning it off and unplugging it from the power source. The thermal paste may harden, and removing the radiator with the cooler cold could damage the processor. Alternatively, you can use a hairdryer with hot air to warm up the needed area.
- Remove the radiator block from the processor. Loosen the screws to ensure even pressure reduction of the radiator on the CPU.
- Apply some alcohol to a lint-free cloth and remove the thermal paste from the radiator. Once the radiator is cleaned, you can check how easily the cooling paste is removed.
- Clean the CPU from the thermal paste using alcohol and cloth. Do not remove the processor and carefully remove the paste. Remaining paste in the crevices can be cleaned with a cotton swab.
- Apply the necessary amount of thermal paste on the processor, waiting for the alcohol to fully evaporate before doing so. Also, ensure there is no liquid, lint, or dust left on the processor.
- Reinstall the cooling radiator block, pressing down on it evenly.
- Screw the cooling radiator back in place, tightening the screws in a diagonal sequence, a few turns at a time. This will help spread the thermal paste evenly across the top of the heat sink.
Upgrade Your Cooling System
If none of the previous tips have helped, it's probably time to replace your CPU's cooling system. This is especially true for owners of hot CPUs from the Ryzen series — acquiring a more efficient system will help reduce the CPU temperature. In most cases, a good tower cooler or a water cooling system can reduce the CPU temperature under load by more than 10 degrees.
Lower the Voltage of the Central Processor
Reducing the power consumption by your processor will have a significant impact on its output temperature. For Intel processors, you can use Intel XTU or Throttlestop programs to reduce the voltage. For AMD processors, you can manually lower the voltage or enable Eco Mode in the AMD Ryzen Master application to significantly reduce the processor's power consumption. However, be aware that switching to AMD Eco Mode in the CPU will lead to an obvious decrease in performance.
Lower the Voltage of the Graphics Card
This action may seem unrelated to the central processor's temperature, however, a discrete graphics card always affects the CPU temperature. In a PC, there is only one component that can heat up as much or even more than the processor — the graphics card. Lowering the voltage of the graphics adapter will reduce the temperature of your processor, especially during gaming. But in some cases, this may lead to a decrease in performance.
- Wie man die CPU-Temperatur in Windows 10 und Windows 11 überprüft
- Prednaročila odprta za prenosnike z AMD 9955HX3D in RTX 5090
- L'Âge du Progrès en Question : Les CPU deviennent plus lents pour la première fois en 20 ans
-
Laptop with an Expandable Display Ranging from 14 to 18 Inches Unveiled
-
Preorders Open for Laptops with AMD 9955HX3D and RTX 5090
-
The Best Gaming CPUs to Buy Right Now: 2025's Top Picks Revealed
-
The Age of Progress in Question: CPUs Get Slower for the First Time in 20 Years
-
How to Check CPU Temperature in Windows 10 and Windows 11