How to Choose a Cooling System for Your PC?

Choosing the right cooling system for your computer is a key factor in ensuring the reliable and productive operation of your device. In this guide, we will look at the main types of cooling systems, their pros and cons, as well as the factors to consider when choosing the optimal solution for your computer.
Importance of a Cooling System
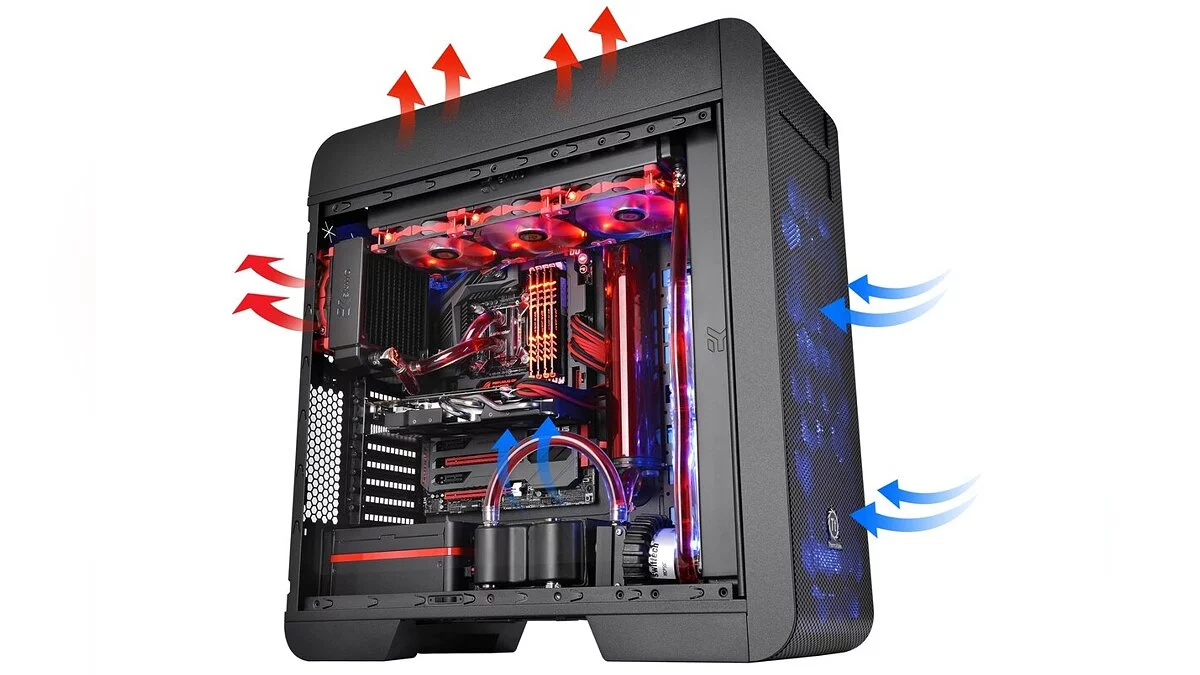
A computer's cooling system plays a crucial role in maintaining its performance and longevity. When components such as the central processing unit (CPU) and graphics processing unit (GPU) perform their tasks, they generate heat. If this heat is not effectively dissipated, thermal throttling can occur, where components slow down to avoid damage, or even hardware failure can happen. A reliable cooling system ensures that all components operate within a safe temperature range, promoting stability and extending the computer's lifespan.
Types of Cooling Systems
There are several types of cooling systems, each with its pros and cons. The main categories include air cooling, liquid cooling, and passive cooling. There are also more specialized methods, such as thermoelectric cooling (Peltier) and phase-change cooling. Each type is suitable for different needs and preferences, ranging from everyday use to high-performance gaming and complex computational tasks.
Air Cooling
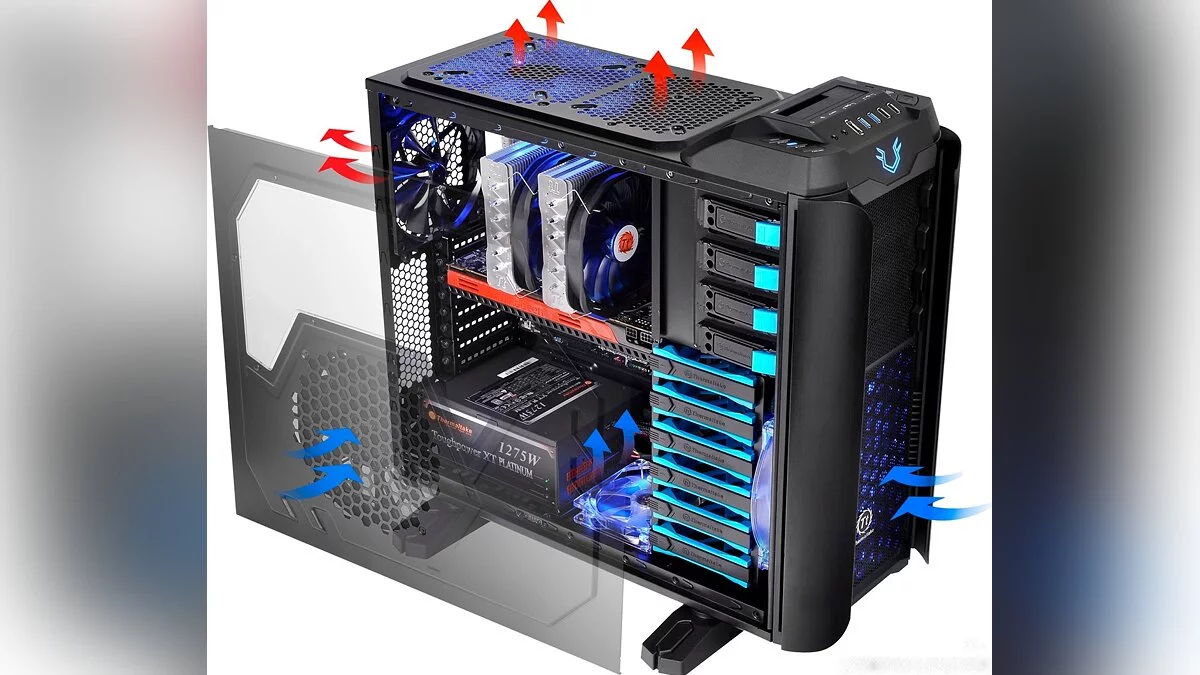
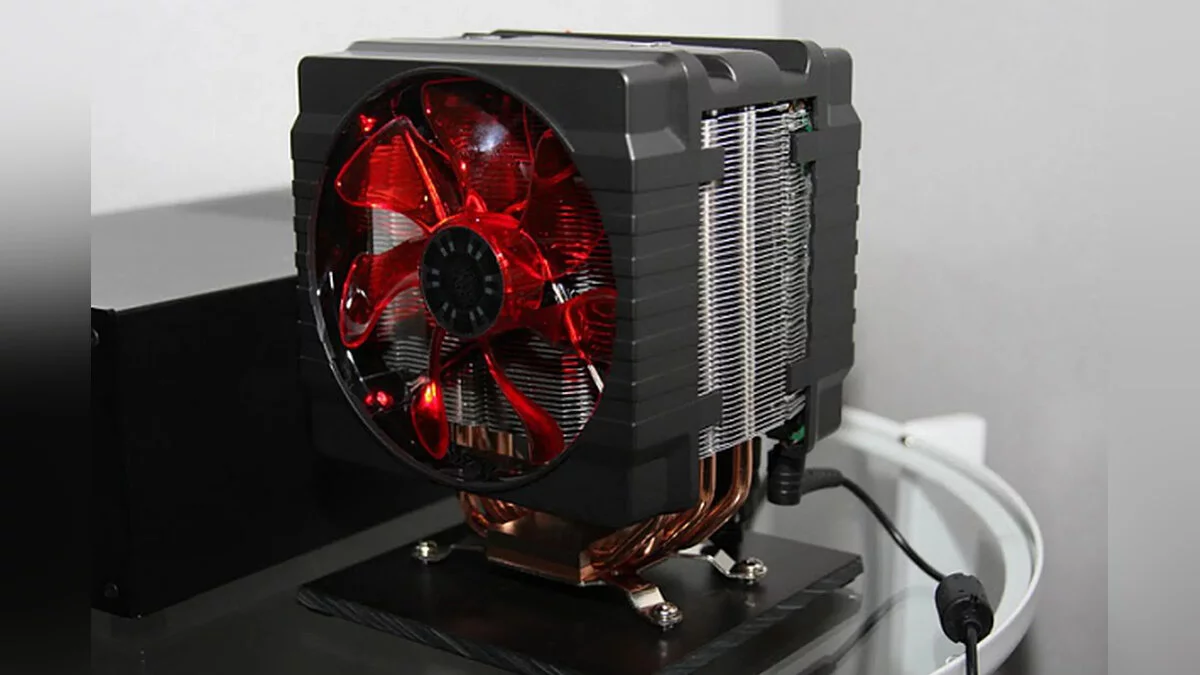
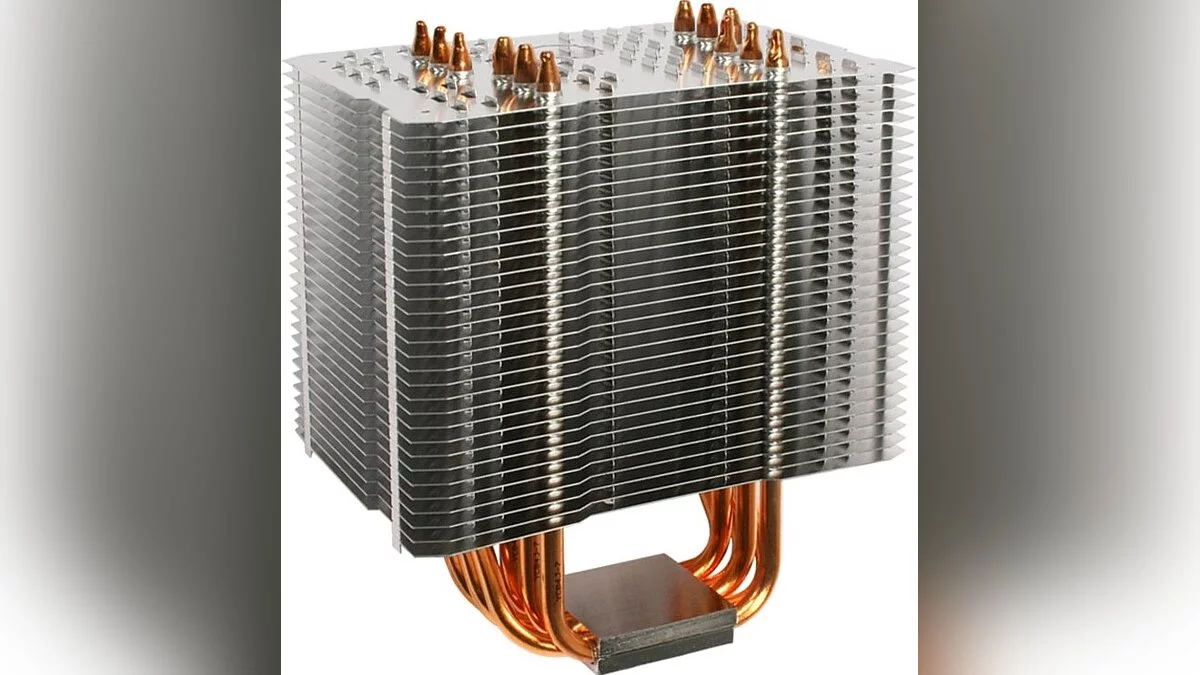
Air cooling is the most common method used in computers. It involves the use of heatsinks and fans to dissipate heat from key components. Copper and aluminum are most frequently used: copper provides better thermal conductivity but is more expensive and heavier. The size and weight of the heatsink also matter, as larger coolers can provide better cooling but may not fit all cases.
Components:
- Heatsinks: These are metal structures attached to the processor and GPU that dissipate heat.
- Fans: They blow air over the heatsinks, carrying heat away from the heatsink.
- Thermal Paste: Applied between the heatsink and the component to improve thermal conductivity.
Fans play a crucial role in air cooling systems. When choosing fans, pay attention to their size (usually 120mm or 140mm), airflow (measured in cubic feet per minute), and noise level (measured in decibels or dBA). Fans with high static pressure are better suited for pushing air through dense heatsinks. Don't forget thermal paste, which ensures good contact between the heatsink and the component, improving heat dissipation. Proper application of thermal paste is essential for optimal performance. Cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and maintenance are the advantages of this type of cooling. However, they can be noisy and less efficient compared to liquid cooling.
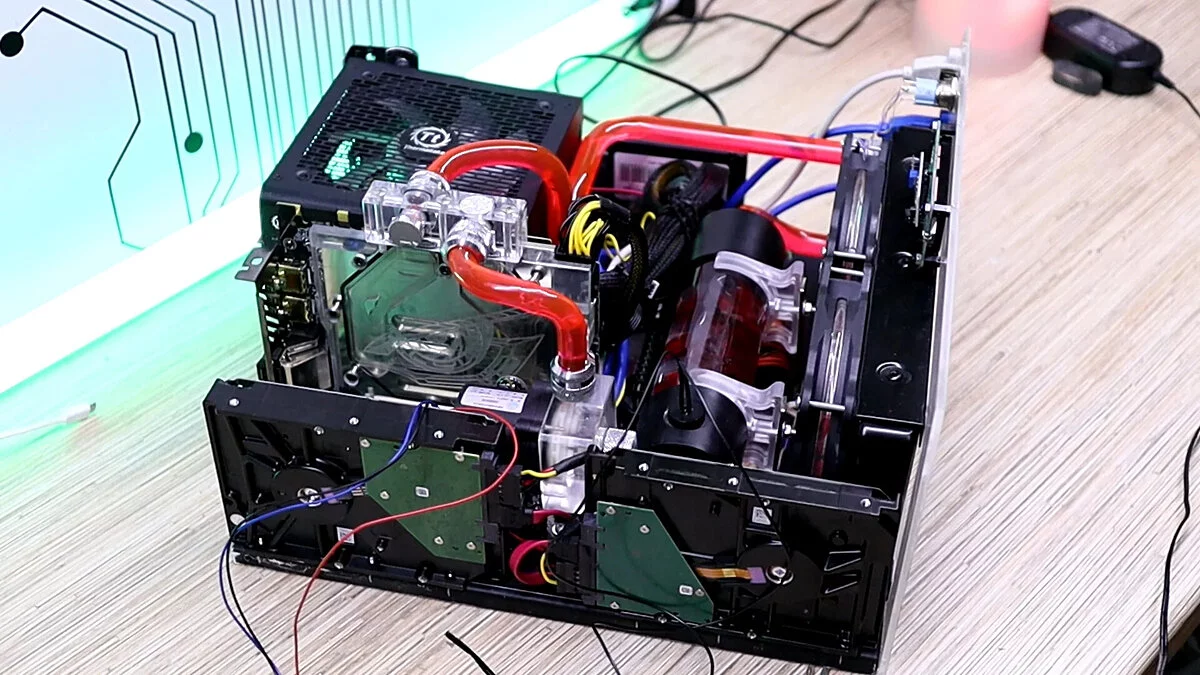
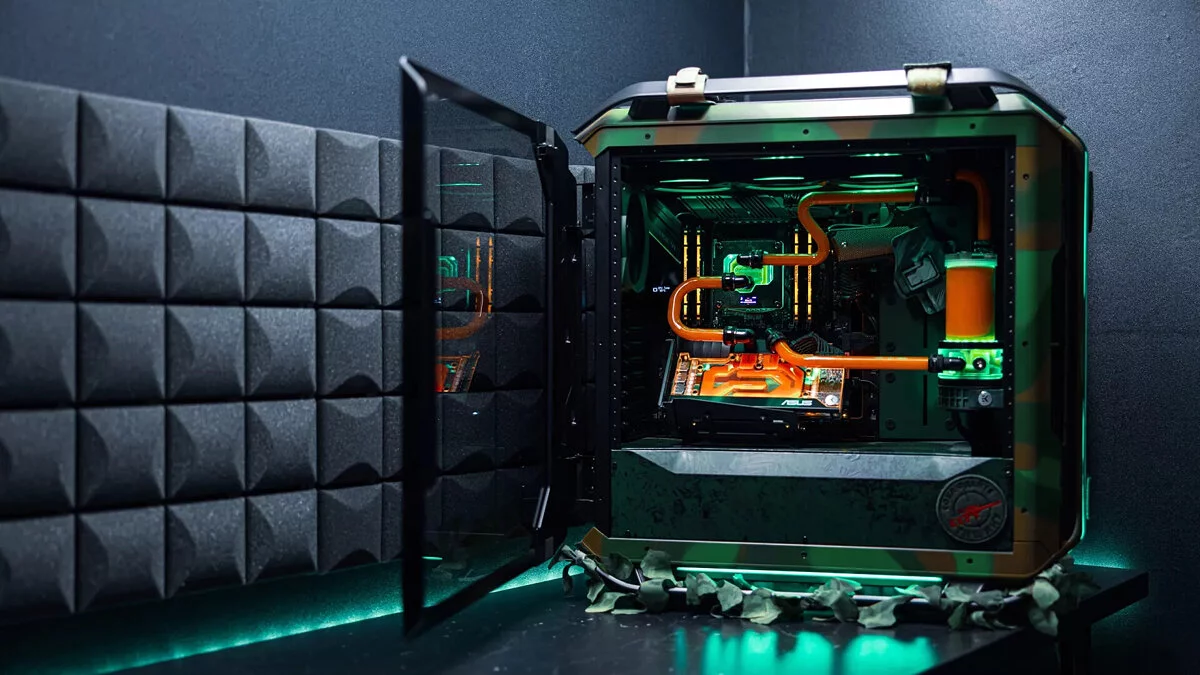
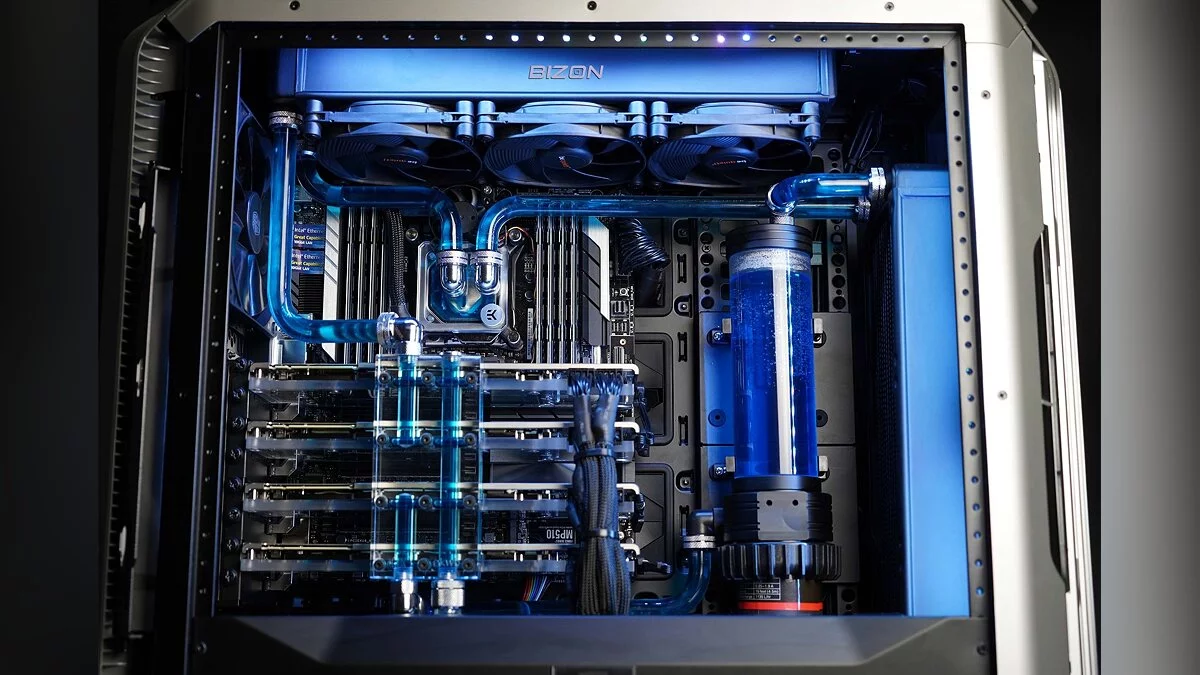
Liquid Cooling
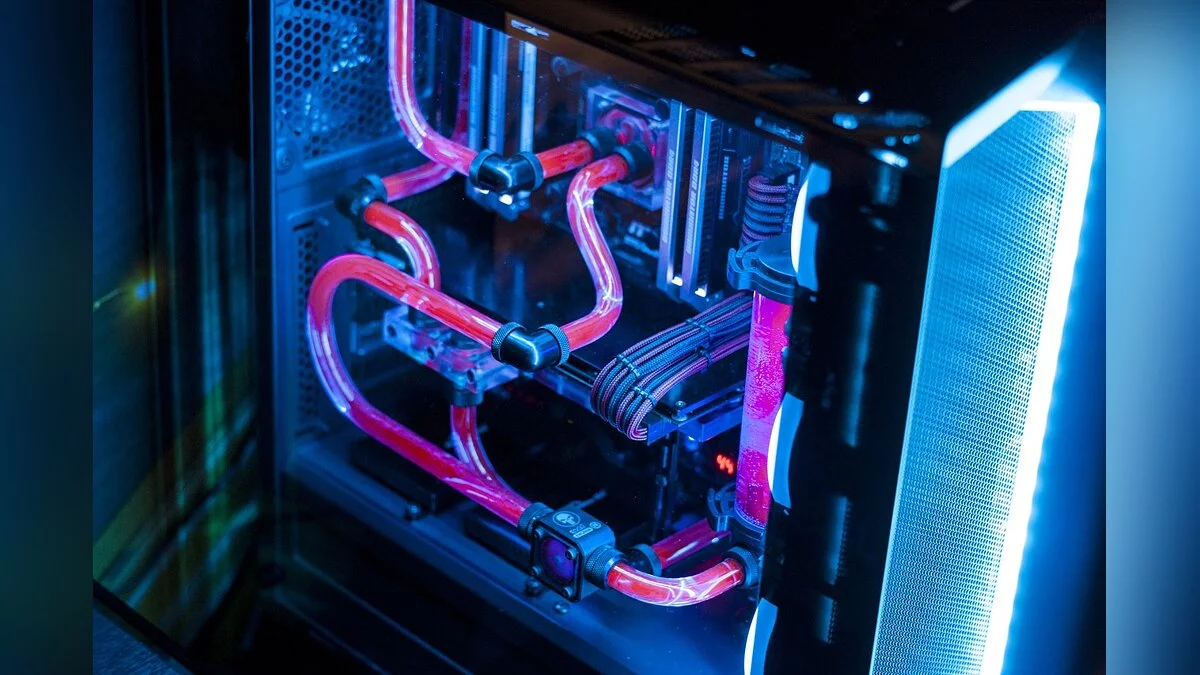
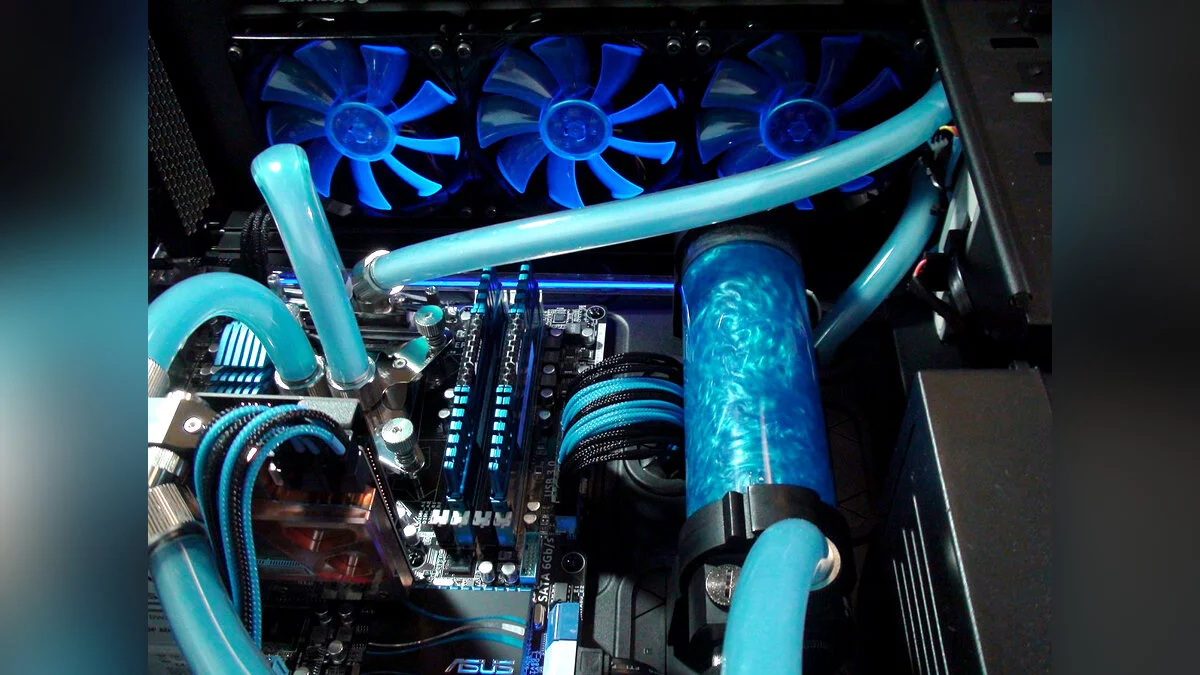
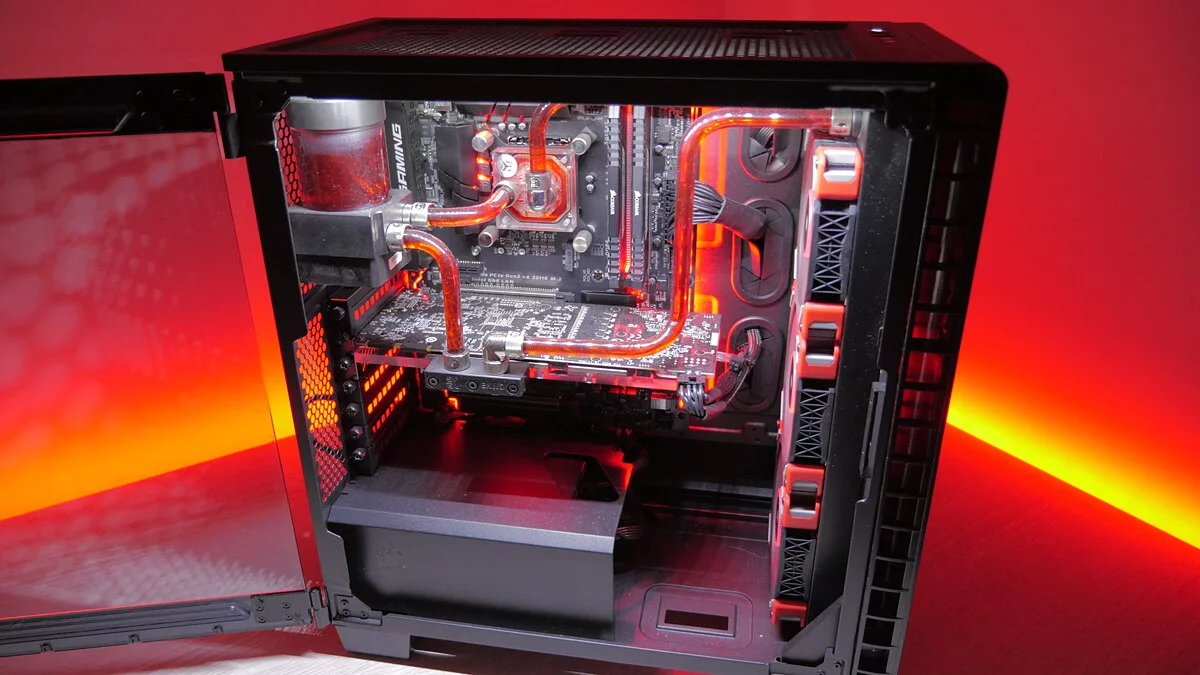
Liquid cooling uses a liquid (usually water) to more effectively dissipate heat from components. It is popular in high-performance and overclocked systems. Liquid cooling provides higher performance compared to air cooling and is a popular choice for high-performance and overclocked systems. Closed-loop or all-in-one (AIO) systems are pre-assembled, making them easier to install and providing excellent cooling. They come in various radiator sizes, such as 120mm, 240mm, and 360mm, which determine how much heat they can dissipate.
Components:
- Radiators: dissipate heat from the liquid into the air.
- Pumps: ensure the circulation of the liquid through the system.
- Water Blocks: absorb heat from the processor and transfer it to the liquid, which then gives off the heat to the radiator.
- Reservoirs: hold extra liquid.
On the other hand, custom loop systems provide the best performance and customization options. They require careful planning and assembly, including choosing the right components such as pumps, reservoirs, and water blocks. Tubing and fittings are also used, depending on the complexity of the setup and aesthetic preferences, which can be either soft or hard. The right choice of coolant is also important, as some coolants provide better thermal performance or longer maintenance intervals.
Installing a liquid cooling system requires certain precautions, such as leak testing the system before powering it on and ensuring good airflow over the radiator. While liquid cooling is more complex, its superior performance and quiet operation make it an attractive option for enthusiasts.
Passive Cooling
Passive cooling is ideal for systems where silence is paramount, such as low-power, silent mini-PCs. It is not used in desktop systems and laptops. These systems rely on natural heat dissipation without the use of fans. Large heatsinks and heat pipes are used to distribute heat over a larger area, allowing it to dissipate naturally.
Components:
- Heatsinks: larger and more efficient at dissipating heat through natural convection.
- Heat Pipes: sometimes used to transfer heat from components to larger heatsinks.
While passive cooling operates almost silently and does not consume power for cooling, its capacity is limited. It is best suited for low-power systems where heat generation is minimal. In more powerful systems, passive cooling may not provide sufficient cooling efficiency, potentially leading to overheating issues.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Cooling System
Choosing the right cooling system for your computer requires careful consideration of several factors. First and foremost, compatibility. It is important to ensure that the cooling system you choose is compatible with your CPU or GPU. Additionally, you need to make sure it fits your motherboard and case. Space and clearance are crucial, as some larger coolers may obstruct other components or simply not fit in your case.
Another important factor is performance requirements. Knowing the estimated thermal design power (TDP) of your CPU and GPU can help you determine the necessary cooling performance. If you plan to overclock your components, you will need a more powerful cooling solution to handle the additional heat output. Noise level is also important; some users prefer silent operation, while others may be more tolerant of noise in exchange for better cooling performance.
Budget is always a decisive factor. Cooling solutions vary greatly in price, from inexpensive air coolers to costly custom liquid cooling loops. It is important to balance cost and performance and decide how much you are willing to invest in your cooling system.
Don't overlook the simplicity of installation and maintenance. Air coolers are generally easier to install and require less maintenance, whereas liquid coolers, especially custom loops, can be more complex to set up and maintain. Finally, aesthetics play a significant role for many users. RGB lighting and customizable components can enhance the look of your build and match your personal style.
Testing and Monitoring Performance
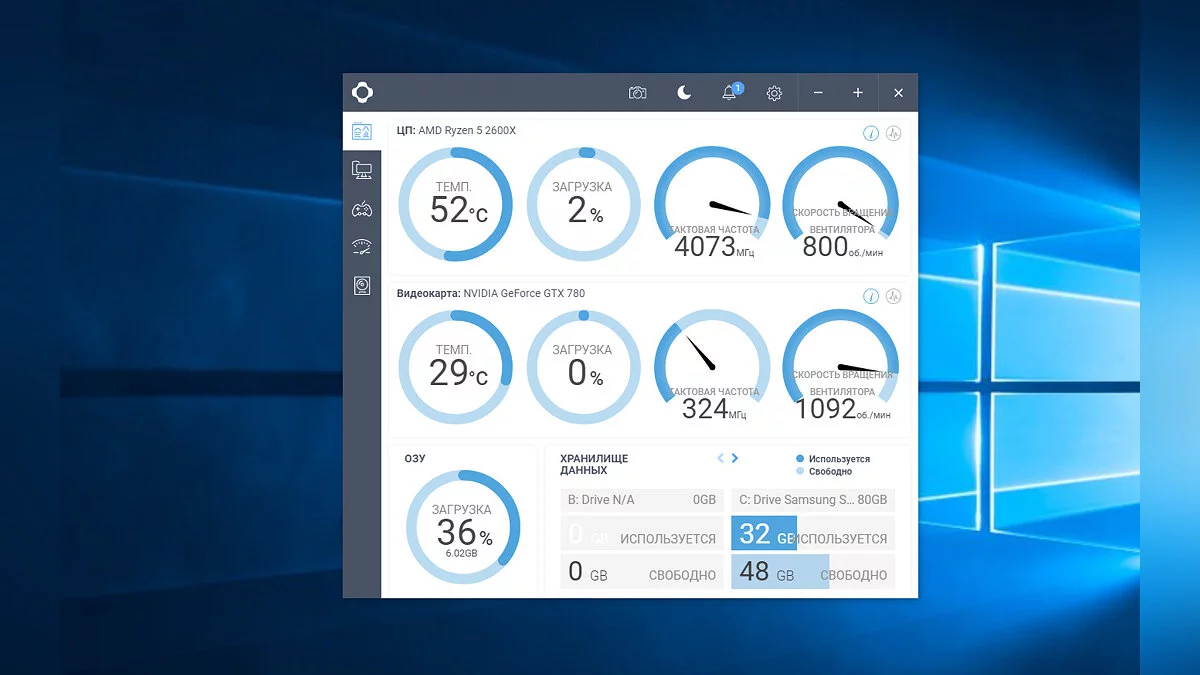
Once you have chosen and installed your cooling system, it is important to test and monitor its performance. Various software tools, such as HWMonitor and AIDA64, can help you track temperatures and other system metrics. Stress-testing your system with programs like Prime95 or FurMark will help you ensure that your cooling solution performs well under high load conditions.
Interpreting these results is crucial. Understanding what temperatures are normal and which are cause for concern can help you make necessary adjustments or improvements to your cooling system. Regular monitoring ensures that your system maintains safe operating temperatures, preventing overheating and hardware damage.
Maintenance Tips
Keeping your cooling system in working order is vital for ensuring long-term operation. Regular cleaning of air coolers is necessary to remove dust that can accumulate on heatsinks and fans, reducing their efficiency. Maintaining fans, such as checking and addressing noise issues, can also help extend their lifespan.
Liquid coolers require more thorough maintenance. The coolant needs to be periodically replaced to prevent degradation and contamination. Checking for leaks and cleaning radiators and blocks are also necessary to maintain optimal performance. Proper maintenance ensures that your cooling system continues to function effectively and reliably.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the best cooling systems can encounter problems. Overheating is a common issue, often caused by dust buildup, insufficient cooling power, or poor airflow. Solutions include cleaning the system, upgrading components, or improving airflow within the case. Noise issues are often related to faulty fans or pumps, which may need to be replaced.
For liquid cooling systems, pump failure can be a serious problem. Symptoms include unusual noise or a sudden increase in temperature. Diagnosing and replacing a faulty pump can prevent further damage to the system. Regular troubleshooting and maintenance will help keep your cooling system in top condition.